Media | Articles
A Gearhead Programmer, an Epic European Road Trip, and the Creation of OutRun
It is 1986. Somewhere, on an unrestricted section of German autobahn, the speedometer of a BMW 5-Series clicks upward, hurtling toward maximum. Inside, two young computer programmers chatter excitedly as the revs rise, the top speed modest by European standards, but double the highest limits in their native Japan. There’s no ticking clock, no announcer shouting “Checkpoint!” But at the wheel is a renegade gearhead and Sega employee, and he’s in the process of creating one of the greatest driving games of all time: OutRun.
Note carefully: that’s driving game, not racing game. Released in 1986 to become almost instantly the most popular arcade game in the world, Sega’s OutRun was all about the feel of driving at high speed, rather than competing against rivals. At the wheel of their own convertible Testarossas, thousands of kids poured in quarter after quarter chasing that thrill.
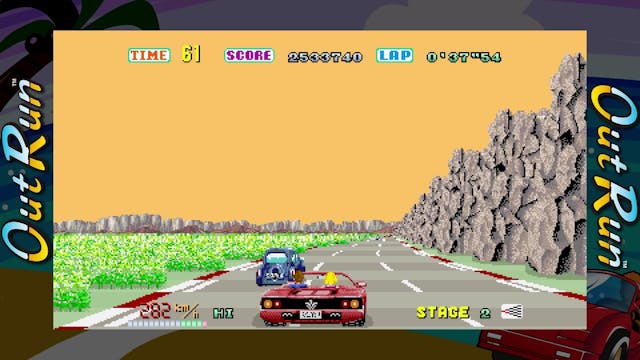
Ferrari’s Testarossa is celebrating its 40th anniversary this year, and it has long been a staple 1980s poster car, rivaled only by the Countach. The most famous example has to be the white 1986 Testarossa that first showed up in the third season of Miami Vice. But the runner up, and arguably more important to a generation, was OutRun’s digitized Testarossa, and its Ferrari roots run deeper than you expect.
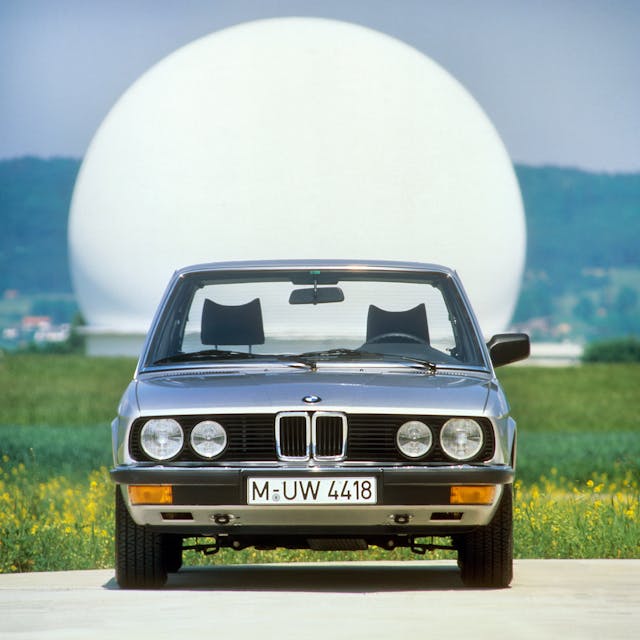

First, an introduction is needed to the Sega employee at the wheel of that BMW 520i. His name is Yu Suzuki, and his influence on video game design over the decades is so vast as to have his Virtua Fighter—one of the first games to use 3D characters—enshrined in the Smithsonian as the only video game on permanent display. But from the very beginning, he never had an interest in playing video games.
“The reason I started making games is I joined a video game company,” Suzuki told Eurogamer in 2015. “That’s it! It’s not like I wanted to be a game designer. I just entered the game company.”
Marketplace
Buy and sell classics with confidence
That company was Sega, and Suzuki was about to hand it the first of a series of hit games. After successfully launching a boxing game, he turned his focus on pushing the limits of technology to create a gaming experience faithful to his love of motorcycles. At the time, Suzuki was mostly interested in motocross and Dakar, but he had expanded into watching circuit racing thanks to the success of American racer Freddie Spencer.
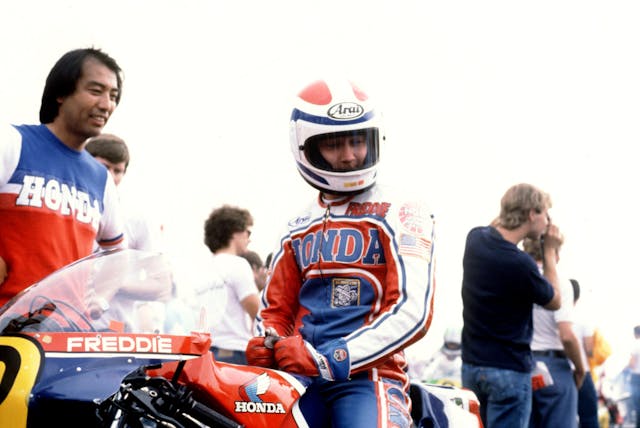

Spencer, who was born in Louisiana, started racing for Honda in the late 1970s, and gave the company its first superbike win in 1980. In 1983, he rode a viciously quick two-stroke Honda NS500 to the 500cc Grand Prix world championship, becoming the youngest-ever rider to do so (Marc Márquez would break this record, but not for three decades). The success of a Japanese motorcycle maker on the world stage came with an explosion of growth in new fans of the sport at home in Japan. Suzuki was among them.
His breakthrough arcade cabinet game was called Hang-On, and it was the first of Sega’s “taikan” games. These were a series of games with hydraulically activated controls, where the cabinet would actually move—action not just on-screen, but in real life. In the case of Hang-On, riders sat on a scale-sized motorcycle and leaned into the turns displayed on a screen in front of the handlebars.
Launched in three styles (a rideable bike plus two simplified versions with just handlebars), Hang-On was projected to sell a few thousand units. Instead, it exceeded expectations by four times, and became Sega’s bestseller. Obviously Sega executives wanted Suzuki to make lightning strike twice. He did, and then some.
Originally, the concept behind OutRun was 1976’s Cannonball Run. Suzuki’s plan was to head to the U.S. and drive from California to Florida, noting the terrain he passed through on the way. Instead, Sega sent him to Europe, along with a superior to keep an eye on things, and a video camera to capture the trip.
In that rented BMW, Suzuki and his project manager, Youji Ishi, started out from Frankfurt with no firm directive other than a need to depart from Rome for Japan in three weeks. They drove Germany’s Romantic Road through Bavaria, crossed into France, traveled through Chamonix to Nice and then Monaco.
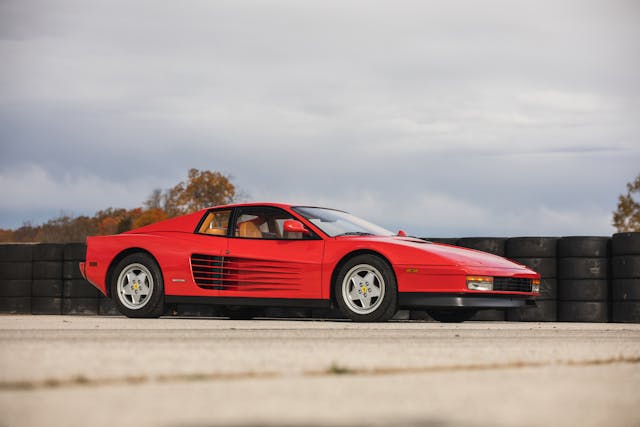

And it was there, in Monte Carlo, that Suzuki found his hero car. After driving the F1 course, he stumbled across a street-parked Testarossa and instantly knew that this was the perfect fit for his game. On return to Japan, he and a small team of artists tracked down one there and photographed it exhaustively for reference.

All this effort to create a series of pixelated sprites may seem overkill, but game designers were pitting their imagination against the limits of technology at the time. Suzuki wanted the feel of high-speed driving to be as accurate as possible, and the exotic shape of the Testarossa would set things off.
OutRun was released in September 1986. By 1987, it was the highest-grossing arcade game in the world, and Sega’s best-ever performer for the entire decade.

In the game, which features a style influenced by digital artist Hiroshi Nagai, players start off on a California-style stage, just as Suzuki had initially planned for his trip. The terrain then transitions to a more European look, heavily based upon the Romantic Road. Tires screech as the terrain rolls and the scenery blurs past. It’s hardly a simulator, but it’s still a thrill to play even now.
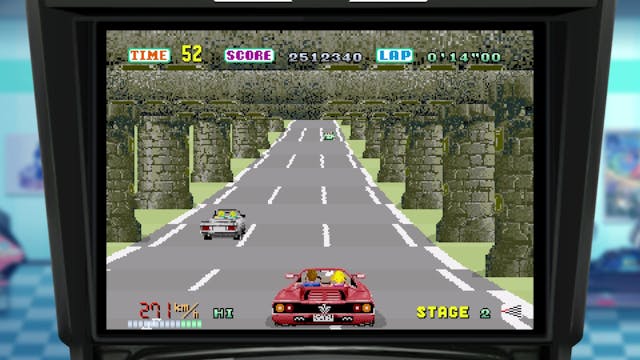
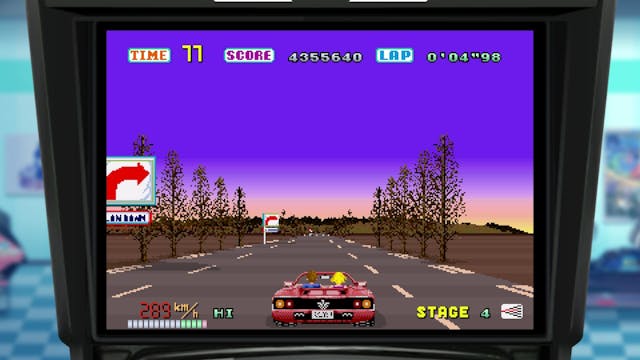
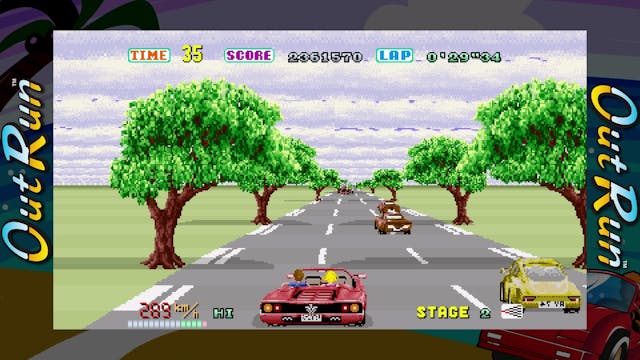
With two knockout hits under his belt, Suzuki was a rockstar at Sega. This was handy, as he was hardly a corporate drone, not the kind to keep to early morning starts and a regimented work week. He formed his own sub-studio, called AM2, away from Sega’s main offices, and he was known for keeping night-owl hours.
Suzuki’s success through the 1980s and 1990s and beyond extended to the point that he was able to buy his own Ferrari, to add to the Ducati and Hayabusa motorcycles he kept in his garage. It wasn’t a Testarossa, but a F355, one of the best-looking cars Maranello ever made.
He would go on to use it to develop another standout automotive arcade game, 1999’s F355 Challenge. This racer was a lot more hardcore simulator than lighthearted OutRun, and it was developed with on-track data collected in Suzuki’s own F355. There are rumors that then-Ferrari F1 racer Rubens Barrichello was so impressed by the game’s accuracy that he even used it to practice a little.

In addition to titles like Daytona and Virtua Racer, F355 Challenge and OutRun cement Yu Suzuki as one of the greatest automotive video game designers of all time, which is to say nothing of the best-selling games in other genres he created. He still says he doesn’t have much time for actually playing games, despite enjoying the work of designing them. He’d rather be riding or driving for real.
But because he tried to make OutRun feel authentic to his genuine passions, Suzuki gave many a kid their first taste of driving freedom. Maybe that kid never grew up to be able to afford a Testarossa, but perhaps an old Alfa Romeo wasn’t entirely out of reach.
So, grab your keys, because that clock never stops ticking. Get out there and hit those checkpoints.
***
Check out the Hagerty Media homepage so you don’t miss a single story, or better yet, bookmark it. To get our best stories delivered right to your inbox, subscribe to our newsletters.





















Wait – what – not a racing game? You wouldn’t have convinced my buddies and me!